depso by Yusuf Tarık Günaydın
NuGet / site data
Details
Info
Name: depso
Package Description
Author: Yusuf Tarık Günaydın
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/depso/
You can find more details at https://github.com/notanaverageman/Depso
Original Readme
Jab Compile Time Dependency Injection
Jab provides a C# Source Generator based dependency injection container implementation.
- Fast startup (200x faster than Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection). Details.
- Fast resolution (7x faster than Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection). Details.
- No runtime dependencies.
- AOT and linker friendly, all code is generated during project compilation.
- Clean stack traces:
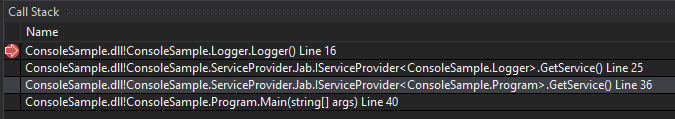
- Readable generated code:
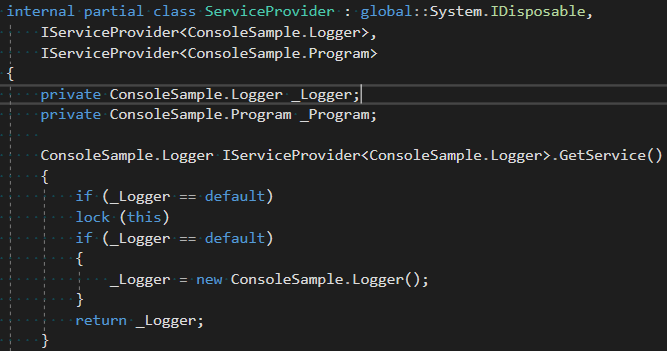
- Registration validation. Container configuration issues become compiler errors:

- Incremental generation, .NET 5/6/7/8 SDK support, .NET Standard 2.0 support, [Unity support](https://github.com/notanaverageman/Depso/README.md#Unity-installation
Example
Add Jab package reference:
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Jab" Version="0.10.2" PrivateAssets="all" />
</ItemGroup>
Define a service and implementation:
internal interface IService
{
void M();
}
internal class ServiceImplementation : IService
{
public void M()
{
}
}
Define a composition root and register services:
[ServiceProvider]
[Transient(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider { }
Use the service provider:
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
IService service = c.GetService<IService>();
Features
- No runtime dependency, safe to use in libraries
- Transient, Singleton, Scoped service registration
- Named registrations
- Factory registration
- Instance registration
IEnumerableresolutionIDisposableandIAsyncDisposablesupportIServiceProvidersupport
The plan is to support the minimum feature set Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.Abstraction requires but NOT the IServiceCollection-based registration syntax as it is runtime based.
Singleton services
Singleton services are created once per container lifetime in a thread-safe manner and cached.
To register a singleton service use the SingletonAttribute:
[ServiceProvider]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider { }
Singleton Instances
If you want to use an existing object as a service define a property in the container declaration and use the Instance property of the SingletonAttribute to register the service:
[ServiceProvider]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), Instance = nameof(MyServiceInstance))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider {
public IService MyServiceInstance { get;set; }
}
Then initialize the property during the container creation:
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
c.MyServiceInstance = new ServiceImplementation();
IService service = c.GetService<IService>();
Named services
Use the Name property to assign a name to your service registrations and [FromNamedServices("...")] attribute to resolve a service using its name.
[ServiceProvider]
[Singleton(typeof(INotificationService), typeof(EmailNotificationService), Name="email")]
[Singleton(typeof(INotificationService), typeof(SmsNotificationService), Name="sms")]
[Singleton(typeof(Notifier))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider {}
class Notifier
{
public Notifier(
[FromNamedServices("email")] INotificationService email,
[FromNamedServices("sms")] INotificationService sms)
{}
}
NOTE: Jab also recognizes the [FromKeyedServices] attribute from Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.
Factories
Sometimes it's useful to provide a custom way to create a service instance without using the automatic construction selection.
To do this define a method in the container declaration and use the Factory property of the SingletonAttribute or TransientAttribute to register the service:
[ServiceProvider]
[Transient(typeof(IService), Factory = nameof(MyServiceFactory))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider {
public IService MyServiceFactory() => new ServiceImplementation();
}
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
IService service = c.GetService<IService>();
When using with TransientAttribute the factory method would be invoked for every service resolution.
When used with SingletonAttribute it would only be invoked the first time the service is requested.
Similar to constructors, factories support parameter injection:
[ServiceProvider]
[Transient(typeof(IService), Factory = nameof(MyServiceFactory))]
[Transient(typeof(SomeOtherService))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider {
public IService MyServiceFactory(SomeOtherService other) => new ServiceImplementation(other);
}
Scoped Services
Scoped services are created once per service provider scope. To create a scope use the CreateScope() method of the service provider.
Service are resolved from the scope using the GetService<IService>() call.
[ServiceProvider]
[Scoped(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider { }
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
using MyServiceProvider.Scope scope = c.CreateScope();
IService service = scope.GetService<IService>();
When the scope is disposed all IDisposable and IAsyncDisposable services that were resolved from it are disposed as well.
Generic registration attributes
You can use generic attributes to register services if your project targets net7.0 or net6.0 and has LangVersion set to preview.
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFrameworks>net7.0</TargetFrameworks>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
Generic attributes allow declaration to be more compact by avoiding the typeof calls:
[ServiceProvider]
[Scoped<IService, ServiceImplementation>]
[Import<IMyModule>]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider { }
Modules
Often, a set of service registrations would represent a distinct set of functionality that can be included into arbitrary
service provider. Modules are used to implement registration sharing. To define a module create an interface and mark it with ServiceProviderModuleAttribute. Service registrations can be listed in module the same way they are in the service provider.
[ServiceProviderModule]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
public interface IMyModule
{
}
To use the module apply the Import attribute to the service provider type:
[ServiceProvider]
[Import(typeof(IMyModule))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider
{
}
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
IService service = c.GetService<IEnumerable<IService>>();
Modules can import other modules as well.
NOTE: module service and implementation types have to be accessible from the project where service provider is generated.
Root services
By default, IEnumerable<...> service accessors are only generated when requested by other service constructors. If you would like to have a root IEnumerable<..> accessor generated use the RootService parameter of the ServiceProvider attribute. The generator also scans all the GetService<...> usages and tries to all collected type arguments as the root service.
[ServiceProvider(RootServices = new [] {typeof(IEnumerable<IService>)})]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
[Singleton(typeof(IService), typeof(ServiceImplementation))]
internal partial class MyServiceProvider
{
}
MyServiceProvider c = new MyServiceProvider();
IService service = c.GetService<IEnumerable<IService>>();
Samples
Console application
Sample Jab usage in console application can be found in src/samples/ConsoleSample
Performance
The performance benchmark project is available in src/Jab.Performance/.
Startup time
The startup time benchmark measures time between application startup and the first service being resolved.
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio | RatioSD | Gen 0 | Gen 1 | Gen 2 | Allocated |
|------- |------------:|----------:|----------:|-------:|--------:|-------:|-------:|------:|----------:|
| MEDI | 2,437.88 ns | 14.565 ns | 12.163 ns | 220.91 | 2.72 | 0.6332 | 0.0114 | - | 6632 B |
| Jab | 11.03 ns | 0.158 ns | 0.123 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.0046 | - | - | 48 B |
GetService
The GetService benchmark measures the provider.GetService<IService>() call.
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio | RatioSD | Gen 0 | Gen 1 | Gen 2 | Allocated |
|------- |----------:|----------:|----------:|------:|--------:|-------:|------:|------:|----------:|
| MEDI | 39.340 ns | 0.2419 ns | 0.2263 ns | 7.01 | 0.09 | 0.0023 | - | - | 24 B |
| Jab | 5.619 ns | 0.0770 ns | 0.0643 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.0023 | - | - | 24 B |
Unity installation
- Navigate to the Packages directory of your project.
- Adjust the project manifest file manifest.json in a text editor.
- Ensure
https://registry.npmjs.org/is part ofscopedRegistries. - Ensure
com.pakrymis part ofscopes. - Add
com.pakrym.jabto the dependencies, stating the latest version.
A minimal example ends up looking like this:
{
"scopedRegistries": [
{
"name": "npmjs",
"url": "https://registry.npmjs.org/",
"scopes": [
"com.pakrym"
]
}
],
"dependencies": {
"com.pakrym.jab": "0.10.2",
...
}
}
Debugging locally
Run dotnet build /t:CreateLaunchSettings in the Jab.Tests directory would update the Jab\Properties\launchSettings.json file to include csc invocation that allows F5 debugging of the generator targeting the Jab.Tests project.
About
generating DI code
How to use
Example (source csproj, source files)
- CSharp Project
- Program.cs
- Database.cs
- DatabaseCon.cs
This is the CSharp Project that references depso
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Depso" Version="1.0.1" />
</ItemGroup>
<PropertyGroup>
<EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>true</EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>
<CompilerGeneratedFilesOutputPath>$(BaseIntermediateOutputPath)\GX</CompilerGeneratedFilesOutputPath>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
This is the use of depso in Program.cs
using InjectDemo;
MyServiceProvider sc = new();
var con = sc.GetService(typeof(Database)) as IDatabase;
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(con);
con.Open();
[Depso.ServiceProvider]
public partial class MyServiceProvider
{
private void RegisterServices()
{
AddTransient<Database, Database>();
AddTransient<IDatabase, DatabaseCon>();
}
}
This is the use of depso in Database.cs
namespace InjectDemo;
partial class Database : IDatabase
{
private readonly IDatabase con;
public Database(IDatabase con)
{
this.con = con;
}
public void Open()
{
Console.WriteLine($"open from database");
con.Open();
}
}
This is the use of depso in DatabaseCon.cs
namespace InjectDemo;
public partial class DatabaseCon:IDatabase
{
public string? Connection { get; set; }
public void Open()
{
Console.WriteLine("open from database con" );
}
}
Generated Files
Those are taken from $(BaseIntermediateOutputPath)\GX
- Depso.Attributes.ServiceProvider.g.cs
- Depso.Attributes.ServiceProviderModule.g.cs
- Depso.MyServiceProvider.g.cs
- Depso.MyServiceProvider.RegistrationMethods.g.cs
- Depso.MyServiceProvider.Scoped.g.cs
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
namespace Depso
{
[global::System.AttributeUsage(global::System.AttributeTargets.Class)]
internal sealed class ServiceProviderAttribute : global::System.Attribute
{
}
}
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
namespace Depso
{
[global::System.AttributeUsage(global::System.AttributeTargets.Class)]
internal sealed class ServiceProviderModuleAttribute : global::System.Attribute
{
}
}
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
public partial class MyServiceProvider
:
global::System.IDisposable,
global::System.IAsyncDisposable,
global::System.IServiceProvider
{
private readonly object _sync = new object();
private global::MyServiceProvider.Scope? _rootScope;
private global::MyServiceProvider.Scope RootScope => _rootScope ??= CreateScope(_sync);
private bool _isDisposed;
public object? GetService(global::System.Type serviceType)
{
if (serviceType == typeof(global::InjectDemo.Database)) return CreateDatabase_0();
if (serviceType == typeof(global::InjectDemo.IDatabase)) return CreateDatabaseCon_0();
if (serviceType == typeof(global::System.IServiceProvider)) return this;
return null;
}
private T GetService<T>()
{
return (T)GetService(typeof(T))!;
}
private global::InjectDemo.Database CreateDatabase_0()
{
return new global::InjectDemo.Database(GetService<global::InjectDemo.IDatabase>());
}
private global::InjectDemo.DatabaseCon CreateDatabaseCon_0()
{
return new global::InjectDemo.DatabaseCon();
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.Scope CreateScope(object? sync)
{
ThrowIfDisposed();
return new global::MyServiceProvider.Scope(this, sync);
}
public void Dispose()
{
lock (_sync)
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
return;
}
_isDisposed = true;
}
if (_rootScope != null) _rootScope.Dispose();
}
public async global::System.Threading.Tasks.ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
lock (_sync)
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
return;
}
_isDisposed = true;
}
if (_rootScope != null) await _rootScope.DisposeAsync();
}
private void ThrowIfDisposed()
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
throw new global::System.ObjectDisposedException("MyServiceProvider");
}
}
}
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
public partial class MyServiceProvider
{
private class RegistrationModifier
{
public static readonly global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier Instance;
static RegistrationModifier()
{
Instance = new global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier();
}
private RegistrationModifier()
{
}
public global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AlsoAsSelf()
{
return this;
}
public global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AlsoAs(global::System.Type type)
{
return this;
}
public global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AlsoAs<T>()
{
return this;
}
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier ImportModule<T>()
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier ImportModule(global::System.Type moduleType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddSingleton(global::System.Type serviceType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddSingleton(global::System.Type serviceType, global::System.Type implementationType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddSingleton<TService>()
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddSingleton<TService, TImplementation>() where TImplementation : TService
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddSingleton<TService>(global::System.Func<global::System.IServiceProvider, TService> factory)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddScoped(global::System.Type serviceType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddScoped(global::System.Type serviceType, global::System.Type implementationType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddScoped<TService>()
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddScoped<TService, TImplementation>() where TImplementation : TService
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddScoped<TService>(global::System.Func<global::System.IServiceProvider, TService> factory)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddTransient(global::System.Type serviceType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddTransient(global::System.Type serviceType, global::System.Type implementationType)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddTransient<TService>()
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddTransient<TService, TImplementation>() where TImplementation : TService
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
private global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier AddTransient<TService>(global::System.Func<global::System.IServiceProvider, TService> factory)
{
return global::MyServiceProvider.RegistrationModifier.Instance;
}
}
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
public partial class MyServiceProvider
{
public class Scope
:
global::System.IDisposable,
global::System.IAsyncDisposable,
global::System.IServiceProvider
{
private readonly object _sync = new object();
private readonly global::MyServiceProvider _root;
private bool _isDisposed;
public Scope(global::MyServiceProvider root, object? sync)
{
_root = root;
if (sync != null)
{
_sync = sync;
}
}
public object? GetService(global::System.Type serviceType)
{
if (serviceType == typeof(global::InjectDemo.Database)) return _root.CreateDatabase_0();
if (serviceType == typeof(global::InjectDemo.IDatabase)) return _root.CreateDatabaseCon_0();
if (serviceType == typeof(global::System.IServiceProvider)) return this;
return null;
}
private T GetService<T>()
{
return (T)GetService(typeof(T))!;
}
public void Dispose()
{
lock (_sync)
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
return;
}
_isDisposed = true;
}
}
public global::System.Threading.Tasks.ValueTask DisposeAsync()
{
lock (_sync)
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
return default;
}
_isDisposed = true;
}
return default;
}
private void ThrowIfDisposed()
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
throw new global::System.ObjectDisposedException("MyServiceProvider.Scope");
}
}
}
}
Useful
Download Example (.NET C#)
Share depso
https://ignatandrei.github.io/RSCG_Examples/v2/docs/depso
aaa
Category "DependencyInjection" has the following generators:
1 AutoRegisterInject 

2 BunnyTailServiceRegistration 

3 DependencyModules.SourceGenerator 

4 depso 

5 FactoryGenerator 

6 FactoryGenerator.Abstractions 

7 Injectio 

8 jab 

9 Pure.DI 

10 ServiceScan.SourceGenerator 




